Advice Articles
These articles provide information on a range of topics relating to horse health. Please scroll down through the articles to find the information you need.
Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance is increasing throughout human and veterinary medicine, and at the same time there are no new classes of antibiotics being produced. This means that there is an increasing population of “superbugs” which are resistant to many or all antibiotics. This may lead to longer recovery times, or in…Read more
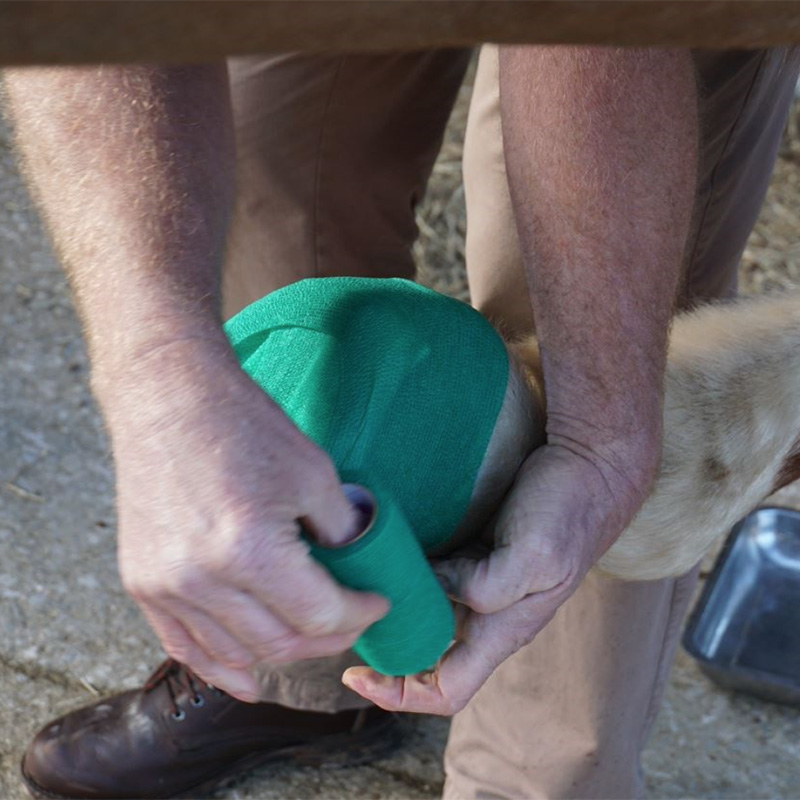
Applying Foot Poultices
The most common reason for very severe lameness in horses is a solar abscess or “pus in the foot”. This is most common after wet weather when the bottom of the foot becomes softer and more likely to be hurt. It is important to get your vet to examine any…Read more
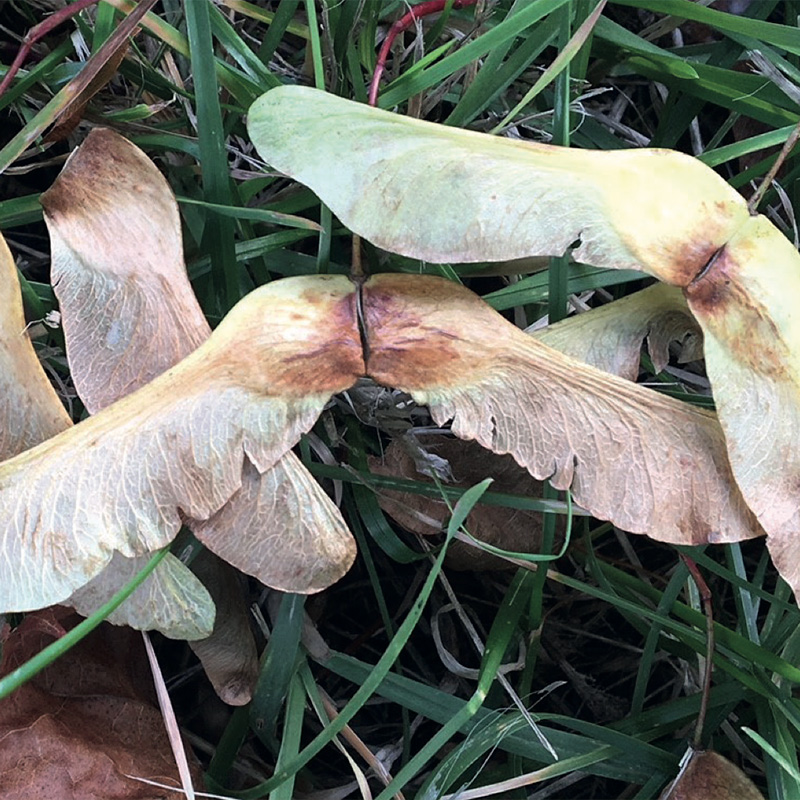
Atypical Myopathy
Atypical Myopathy (also known as ‘Sycamore Poisoning’) is a severe and potentially fatal muscle disorder of horses caused by eating Sycamore ‘helicopter’ seeds and, to a lesser extent Sycamore leaves, that fall onto pasture in the autumn & winter or Sycamore seedlings which grow in the Spring. The seeds and…Read more
Behavioural Problems in Performance Mares
Behavioural problems in performance mares are common and can arise from a variety of reasons. Behaviour considered undesirable in the performance mare, although rarely, can be due to: Normal oestrus cycle activity Abnormal oestrus cycle activity Non reproductive cycle factors Types of behavioural problems The range of behavioural problems in performance mares…Read more
Box Rest Advice
Box rest can be stressful for both the horse and the owner. We have put together some basic advice to try to keep you both sane, but if you are struggling to box rest your horse, please don’t be afraid to contact us for further advice. Feeding Your horse will only require…Read more
Caring for Your Horse in Hot Weather
Hot weather has its own range of challenges for you and your horse. Making sure that they don’t get dehydrated or struggle to deal with the heat is important. Water A 500kg horse needs to drink 25 Litres of water daily in normal weather. This only goes up when the weather becomes…Read more
Castration
Colts are generally castrated for ease of management. If a colt is left entire it is usually impractical/impossible to run them in company, with either mares, geldings or other stallions, especially as they mature. They can become difficult to handle, and in some cases, can be so dangerous as to…Read more
Choke
What Is It? ‘Choke’ can be a very scary experience for owner and horse alike. The name is misleading, as it refers to an obstruction (usually food) in the oesophagus (food pipe) rather than the trachea (wind pipe). The most common sign of choke is sudden coughing, wretching and discomfort immediately after…Read more
Colic
How to recognise it and what to do Colic is a term used to describe abdominal pain and can vary from being mild and short lived to severe and life threatening. Colic symptoms usually indicate a problem with the gastrointestinal system, however, other abdominal organs such as liver, kidneys, spleen or…Read more
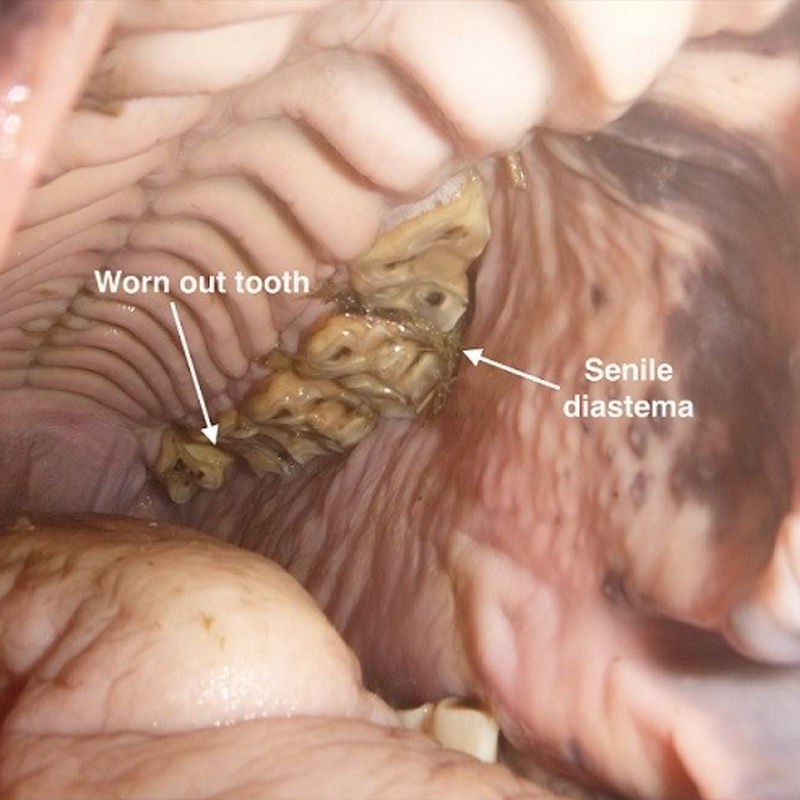
Dentistry
Horses, ponies, and donkeys are herbivores that have evolved to graze for long periods and one of their key adaptations is a set of hardwearing and specialised teeth that enable them to process forage efficiently throughout their lives. What sort of teeth do horses have and how do they differ…Read more
Ectoparasites
Flies There are several ‘types’ of fly, which can prove a torment to horses during spring and summer months. Biting flies can pierce the horse’s skin and feed on its blood, while nuisance flies lay secretions in and around the horse’s eyes, mouth, nose and other sensitive areas. Aside from…Read more
Equine Herpes Virus (EHV)
Although there are in fact 5 different equine herpesviruses (EHV 1-5), the one we see most commonly associated with disease in horses is EHV-1, which can cause respiratory disease, abortions and neurologic disease. Briefly, the other EHVs are: EHV-2: Rarely causes disease. EHV-3: This is the cause of a disease called coital…Read more
Equine Asthma
Equine asthma (EA) is the new name given to a common respiratory disease that affects horses and ponies. Previous names have included Recurrent airway obstruction (RAO), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and ‘heaves’. The disease is similar to asthma in humans, hence the new name, and is a common reason…Read more
Equine Gastric Ulceration
What is gastric ulceration and why does it happen? Equine Gastric Ulceration Syndrome (EGUS) is a common disease affecting the equine stomach. The horse’s stomach is divided into two very distinct areas, the non-glandular/squamous region and the glandular region, which are separated by a sharp demarcation called the margo plicatus.…Read more
Equine Grass Sickness
Equine grass sickness (EGS) is a disease of the nerves that coordinate intestinal movement, which causes the digestive system to stop functioning properly. What is the cause of EGS? For many years the cause of the disease was unknown, but it is now thought that toxins released from the bacteria Clostridium Botulinum cause…Read more
Equine Influenza (Flu)
This is a highly contagious viral disease of the upper and lower respiratory tracts. There are many different strains of the flu virus, the most common ones seen in this country are H7N7 and H3N8. Whilst equine flu is now endemic within the horse population, the virus strains continually mutate…Read more
Equine Metabolic Syndrome
Equine Metabolic Syndrome (EMS) is veterinary term to describe horses and ponies who suffer from obesity, insulin resistance and are at an increased risk of laminitis. Some breeds of horse and pony are at risk of developing EMS because they have evolved to survive in harsh environments. The native pony…Read more
Euthanasia and Disposal
We all keep our horses for a variety of reasons, from companions through to competition horses. In doing so, we take on the responsibility for caring for our horse such as providing food, water, shelter, healthcare, and treatment when necessary. Another responsibility we have as horse owners, which we often…Read more
Euthanasia - When is the right time to say goodbye
It’s always that difficult question when you have an older horse or pony. They are getting progressively stiffer and struggling to hold their condition as well as they used to. You start to ask yourself, is it time to let them go? Sometimes, the decision is taken out of our…Read more
Fireworks
We all know that horses and fireworks can be a difficult combination to manage. As bonfire night approaches make sure you take precautions to minimise the impact they have on your horse or pony. Find out if there are any commercial displays planned near to where your horse is kept,…Read more
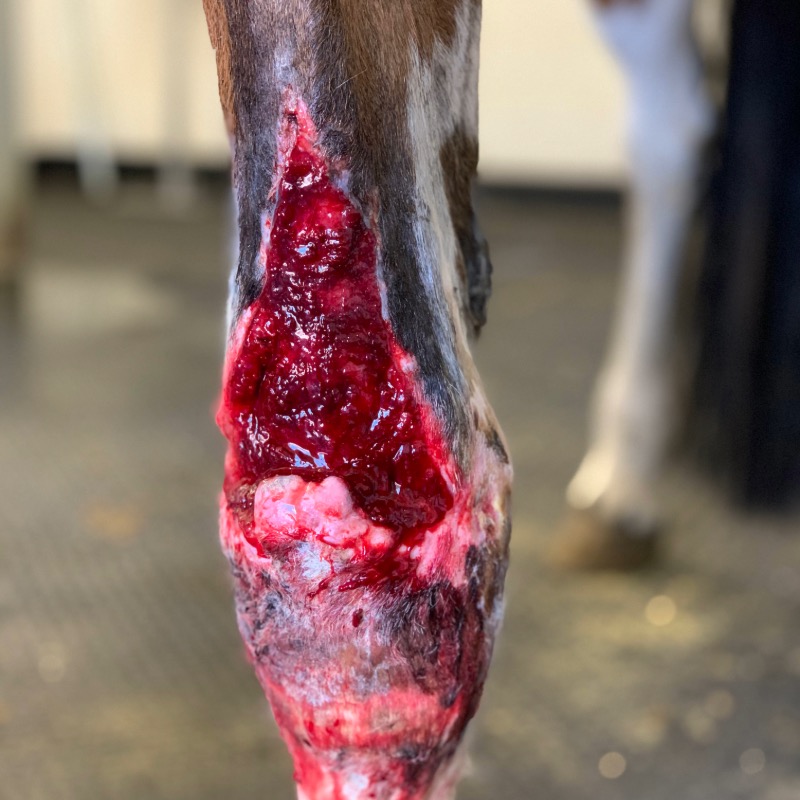
First Aid for Wounds
Skin wounds are extremely common in horses, particularly on the limbs or face. Many wounds only require simple first aid to treat them, though more serious ones will require veterinary attention. Arming yourself with some basic first aid knowledge and a suitable first aid kit will enable you to treat…Read more
Foaling
Most mares foal normally without assistance, however, if the mare does have difficulty, the foal and mare can become compromised very quickly. Mares have a very variable pregnancy length, the average mare pregnancy lasts between 335 and 340 days, the mare usually starts to develop an udder around 2 weeks…Read more
Hoof Abscesses
What is it? A hoof abscess describes a painful build-up of purulent material (pus) within the hoof capsule. It will often be extremely uncomfortable for the horse, causing an obvious lameness at walk. Foot abscesses are caused by bacteria entering the hoof capsule and setting up an infection. The bacteria can…Read more
Kissing Spines
Back pain in horses is fairly common. It can either be primary, associated with the bones in the spine, or secondary i.e. muscular pain secondary to a poor fitting saddle, low grade lameness causing muscle tension and a restricted gait or lack of top line. Primary back pain is most…Read more
Laminitis
What is Laminitis? Laminitis means inflammation of the laminae within a horse’s foot. The laminae are delicate structures which form the junction between the hoof wall and the pedal bone inside the foot. Inflammation of the laminae weakens them, causing the pedal bone to become unstable within the horse’s foot.…Read more
Liver Disease
The liver is one of the largest organs in the body and has an essential role in a wide variety of bodily functions. These include modification and utilisation of nutrients absorbed from the intestines to provide energy for the body’s cells, removing toxins and waste products from the blood stream…Read more
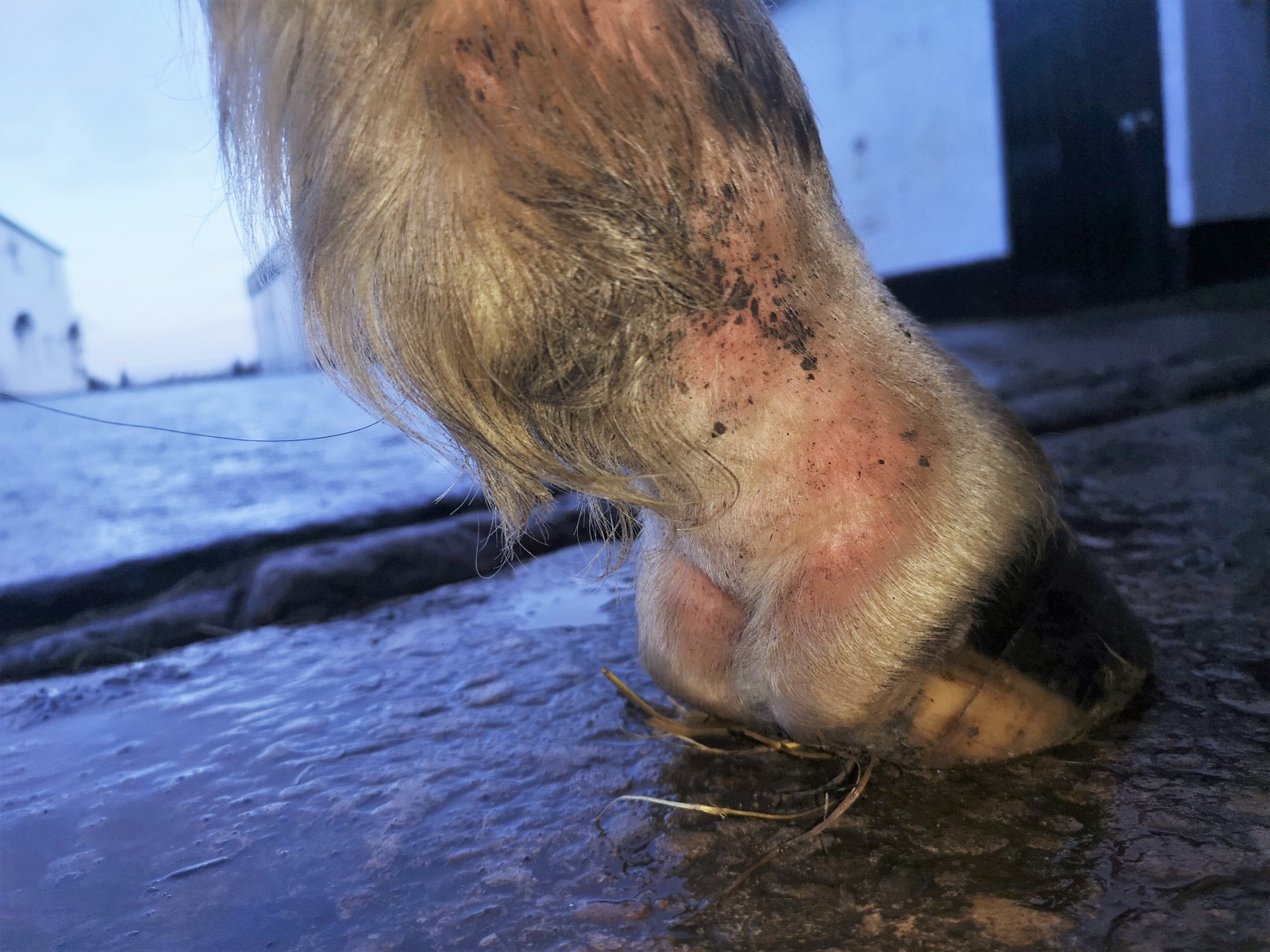
Mud Fever
Mud fever is a year round problem. Traditionally it has been associated with wet muddy conditions seen in the winter but we often see cases throughout the year. What is Mud Fever? Mud fever, also known as pastern dermatitis or ‘cracked heels’ is a skin condition generally caused by a bacteria called…Read more
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthriitis is characterised by degeneration and loss of normal cartilage and inflammation within a joint. ‘Osteoarthritis’ comes from the Greek words oeteo (bone) arthron (joint) and the suffix ’itis’ means inflammation. Joints are found where two bones meet and are made up of layers of connective tissue and fluid which…Read more
PPID (Cushing's)
What is PPID? PPID is often called Equine Cushing’s Disease (ECD). It is an endocrine disorder that occurs in over 20% of aged horses, ponies, and donkeys. Most horses are over 15 years of age when they are diagnosed, and it is very rare in horses younger than 10. Why…Read more
Preventative Healthcare
Preventative healthcare has a host of benefits for you and your horse. As well as doing everything possible to reduce the risk of diseases such as influenza, tetanus and worm-related conditions, it also allows an opportunity for your vet to check your horse over for any other issues and address…Read more
Sarcoids
What are Sarcoids? Sarcoids are a relatively common tumour seen in horses of all kinds. although they generally cause no major health problems because they are limited to spreading on the skin alone, the presence of sarcoids can cause irritation, problems with tack and a loss of value if selling your…Read more
Sheath Examination
What is the sheath and what does it look like normally? The term sheath describes the pocket of skin around your horse's penis. Unless your horse is relaxed or urinating, its penis will usually be retracted, and you won't be able to see the sheath. Over time, skin secretions and dead…Read more
Splints
What are they? ‘Splints’ refer to a hard, boney swelling that appears on the inside (or occasionally outside) of the horse’s lower leg. They are caused by damage to the splint bones or the ligament between the splint and cannon bone. They are common in younger horses in training but can…Read more
Strangles
What is Strangles Strangles is a highly contagious, bacterial infection of the upper respiratory tract caused by Streptococcus equi equi. The disease can affect horses, ponies and donkeys of all ages. Although the disease can make affected horses quite unwell for a couple of weeks, most make a full recovery.…Read more
Supplements
The market for supplements is huge and many owners find different supplements useful for caring for their horse but it is easy to become overwhelmed by the vast number of options available for your horse. Manufacturers of supplements do not have to tell you how much of an active ingredient is…Read more
Tendon and Ligament Injuries
Tendon Injuries Tendons are the strap-like elastic structures that attach muscles to the bones on which they act. Most tendons are relatively short and are rarely damaged. However, the long tendons of the limbs are vulnerable to damage during exercise or as a result of trauma. The flexor tendons are the…Read more
Tetanus
Tetanus is caused by the bacterium Clostridium Tetanii which is an anaerobic organism (does not need oxygen). It survives in the environment (soil and droppings) for long periods of time. Tetanus is not contagious, meaning it cannot be spread horse to horse. Tetanus penetrates the body via wounds. Puncture wounds…Read more
Equine Vaccinations
Horses, ponies and donkeys are susceptible to a number of diseases, some of which we can vaccinate against. What is a vaccination? A vaccination is a way of producing an immune response against a specific disease. It primes the immune system so that an appropriate immune response can be stimulated if your…Read more
Weight Management
Our horse is an amazing product of evolution. Over thousands of years they have developed to survive on the sides of mountains with little food pursued by all sorts of predators. This means that they do a little too well when we provide them with a life of luxury, food…Read more
Wet Weather Management
Very wet and muddy conditions can cause a variety of problems. Over the last few years, we have had milder winters, which often results in wet and muddy conditions. We have compiled some topical tips on managing your horse in wet weather. Many yards keep horses stabled due to waterlogged fields, but this can be a big…Read more